A catalytic converter is a critical component of your vehicle’s exhaust system. It reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic pollutants from your engine into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere. However, like any car part, catalytic converters can wear out or fail over time. But what happens when a catalytic converter fails?
In this blog post, we’ll explore what happens when a catalytic converter fails, the symptoms of failure, and how it can impact your vehicle’s performance. Understanding these signs and taking action early can help you avoid costly repairs and keep your vehicle running efficiently.
The Function of a Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is located between the engine and the muffler in your vehicle’s exhaust system. It contains a honeycomb structure coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts, promoting chemical reactions that convert harmful gases like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful gases such as carbon dioxide and water vapor.
A properly functioning catalytic converter helps reduce the pollutants that your car emits, ensuring that it complies with emissions standards. When the converter fails, however, it can no longer effectively perform this function, leading to a variety of issues.
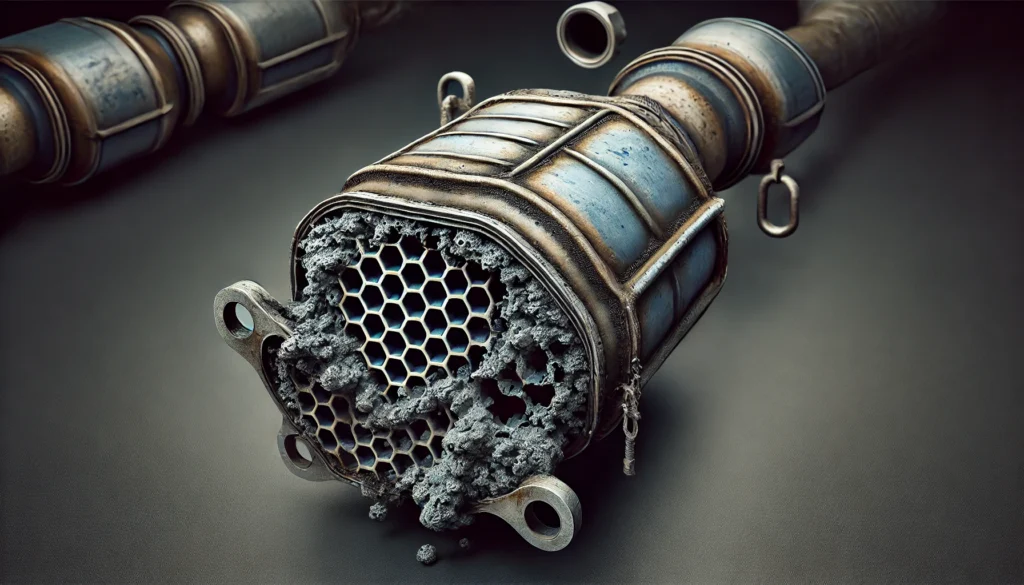
Symptoms of a Failed Catalytic Converter
When a catalytic converter begins to fail, there are several warning signs that can help you identify the problem early. Here are the most common symptoms of a failed catalytic converter:
- Check Engine Light: One of the first signs that something is wrong with your catalytic converter is the check engine light. The onboard diagnostics system monitors the performance of the catalytic converter, and if it detects that the converter isn’t working properly, it will trigger the check engine light.
- Poor Engine Performance: A failing catalytic converter can cause your engine to struggle. You may experience reduced acceleration, difficulty maintaining speed, or even stalling while driving. This occurs because the exhaust gases can’t pass through the clogged or damaged converter, creating backpressure in the system and forcing the engine to work harder.
- Rattling Sounds: Inside the catalytic converter is a ceramic honeycomb structure that can break apart if the converter is failing. When this happens, you might hear a rattling noise when your vehicle is idling or accelerating.
- Increased Emissions: One of the key functions of a catalytic converter is to reduce harmful emissions. When it fails, it can no longer effectively convert toxic gases, leading to increased emissions. You may notice dark smoke coming from the exhaust or even a foul sulfur smell (often described as a “rotten egg” odor) due to unprocessed sulfur compounds being released.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A failing catalytic converter can reduce your vehicle’s fuel efficiency. The engine must work harder to push exhaust gases through the clogged or damaged converter, which increases fuel consumption and leads to lower gas mileage.
What Happens When Catalytic Converter Fails?
When a catalytic converter fails, it can have a range of effects on your vehicle’s performance and overall health. Here’s what happens:
- Increased Emissions: When the catalytic converter fails, it can no longer reduce harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases. This leads to increased emissions, which not only contribute to environmental pollution but can also cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test. In many states and regions, failing an emissions test means that your car cannot be legally driven until the problem is fixed.
- Engine Damage: If a catalytic converter becomes clogged, it can cause backpressure in the exhaust system. This backpressure can force exhaust gases back into the engine, leading to overheating and potentially severe engine damage. In extreme cases, the increased pressure can cause the engine to misfire or even fail completely.
- Reduced Vehicle Performance: A failing catalytic converter can significantly reduce your vehicle’s overall performance. You may notice sluggish acceleration, difficulty maintaining speed, or even stalling when driving. This is due to the converter’s inability to properly process exhaust gases, which interferes with the engine’s ability to operate efficiently.
- Failed Emissions Test: If your catalytic converter fails, your vehicle is unlikely to pass an emissions test. In regions with strict emissions regulations, this can result in your vehicle being deemed unfit for the road. In some cases, it may even be illegal to drive your car until the issue is resolved.
- Potential Fire Hazard: In rare cases, a failed catalytic converter can become a fire hazard. If the converter overheats, it can ignite nearby flammable materials, such as oil or fuel, leading to a dangerous situation.
Causes of Catalytic Converter Failure
Several factors can cause a catalytic converter to fail. Understanding these causes can help you prevent problems in the future:
- Contaminants in the Exhaust System: Contaminants such as oil or antifreeze can enter the exhaust system and damage the catalytic converter. These substances can coat the converter’s internal honeycomb structure, preventing it from working effectively.
- Unburned Fuel: When there is an issue with the fuel-to-air ratio in the engine, unburned fuel can enter the exhaust system. This unburned fuel can ignite inside the catalytic converter, causing it to overheat and fail.
- Short Trips: Frequently driving short distances or making cold starts can contribute to catalytic converter failure. The converter needs to reach a high operating temperature to function effectively, and if it doesn’t, it can become clogged with carbon deposits over time.
- Physical Damage: Catalytic converters are located underneath the vehicle, making them vulnerable to damage from road debris or improper installation. Physical damage to the converter’s exterior shell can lead to internal failures and reduce its effectiveness.
How to Prevent Catalytic Converter Failure
Taking steps to maintain your vehicle and prevent catalytic converter failure can save you from expensive repairs in the future. Here are some tips to keep your catalytic converter in good condition:
- Regular Maintenance: Regular engine maintenance is crucial to preventing catalytic converter failure. This includes replacing spark plugs, changing oil, and keeping the fuel and air mixture balanced. A well-maintained engine is less likely to produce the unburned fuel or excess contaminants that can damage the converter.
- Fix Leaks Promptly: If you notice any oil or coolant leaks, have them repaired as soon as possible. Contaminants from leaks can enter the exhaust system and damage the catalytic converter.
- Drive Longer Distances: Avoid making frequent short trips that don’t allow the engine to fully warm up. Longer drives give the catalytic converter enough time to reach its optimal operating temperature and burn off any accumulated deposits.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel with cleaning additives can help reduce the buildup of contaminants in the exhaust system. Premium fuels often contain detergents that help keep the engine clean and reduce the risk of catalytic converter failure.
What to Do If Your Catalytic Converter Fails
If you suspect that your catalytic converter has failed, it’s important to take action quickly to prevent further damage to your vehicle. Here are the steps you should take:
- Get a Diagnostic Test: If your check engine light is on or you notice any of the symptoms of a failed catalytic converter, take your vehicle to a mechanic for a diagnostic test. They will be able to determine if the converter has failed and recommend the necessary repairs.
- Replace the Catalytic Converter: If your catalytic converter has failed, it will need to be replaced. In most cases, a full replacement is necessary to restore your vehicle’s performance and ensure that it meets emissions standards.
- Address Underlying Issues: If the catalytic converter failed due to engine problems such as misfires or unburned fuel, it’s important to fix the underlying issue to prevent future converter failure.
Conclusion
A failing catalytic converter can lead to a variety of issues, including reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage. Recognizing the signs of catalytic converter failure early and taking prompt action can help you avoid more serious problems and costly repairs.
Understanding what happens when a catalytic converter fails is key to maintaining your vehicle’s performance and ensuring that it meets emissions standards. By staying on top of engine maintenance, addressing leaks and other issues promptly, and driving in a way that supports your catalytic converter’s function, you can extend its lifespan and prevent failure.
