The catalytic converter is an essential part of your vehicle’s exhaust system, designed to reduce harmful emissions and keep your engine running efficiently. However, like any component, it can experience wear and tear over time. One common issue is a clogged catalytic converter, which can lead to engine problems, decreased performance, and even potential damage to other parts of your vehicle.
So, can a catalytic converter be clogged? Absolutely. In fact, clogged catalytic converters are a frequent issue in vehicles, especially older models or those that have not been properly maintained. In this article, we’ll explain how a catalytic converter can become clogged, the symptoms you should look out for, and what you can do to fix or prevent this issue.
What Causes a Catalytic Converter to Become Clogged?
The catalytic converter works by converting harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful emissions like carbon dioxide and water vapor. This process takes place as exhaust gases pass through a honeycomb structure coated with precious metals, which act as catalysts for chemical reactions.
Over time, this honeycomb structure can become coated with carbon deposits or other contaminants that prevent it from functioning efficiently. Additionally, engine problems such as misfires, oil leaks, or a rich fuel mixture can also lead to a clogged catalytic converter. Here’s a breakdown of the most common causes:
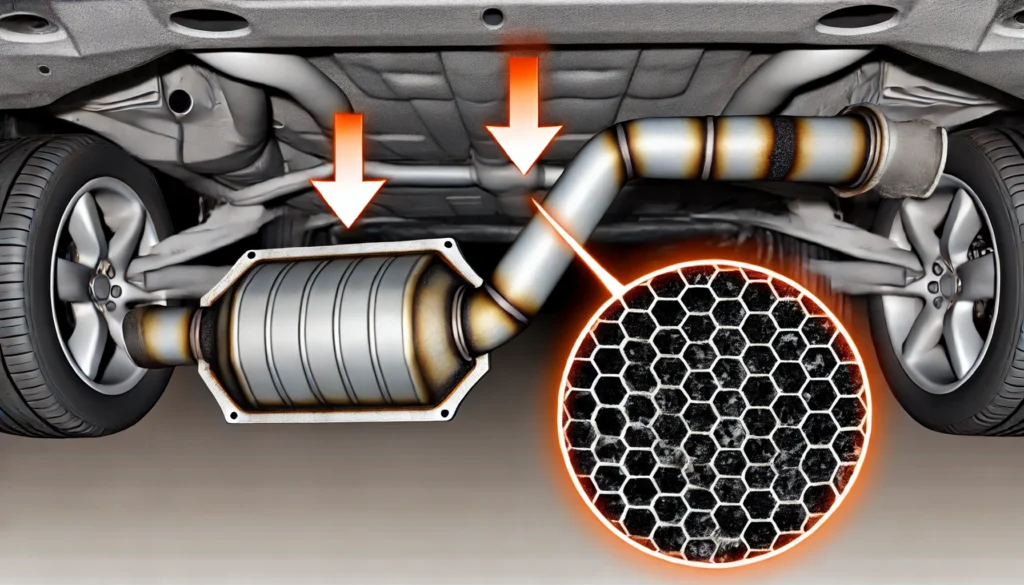
1. Carbon Buildup
Carbon deposits can form inside the catalytic converter, especially if the vehicle is running rich (burning too much fuel) or if it frequently idles in traffic. These carbon deposits can block the flow of exhaust gases, reducing the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
2. Engine Misfires
Misfires cause unburned fuel to enter the exhaust system, which can then burn inside the catalytic converter. This excess heat can cause the converter’s honeycomb structure to melt or become damaged, leading to clogging.
3. Oil or Coolant Leaks
If oil or coolant leaks into the combustion chamber, it can contaminate the catalytic converter and cause clogging. Oil or coolant entering the exhaust system creates a sticky residue that blocks the converter’s pathways and prevents the proper flow of exhaust gases.
4. Excessive Fuel Consumption
A faulty oxygen sensor or fuel injector can cause the engine to run rich, meaning there’s too much fuel in the air-fuel mixture. When excess fuel enters the exhaust system, it can coat the catalytic converter with soot or carbon, leading to a blockage.
Symptoms of a Clogged Catalytic Converter
If your catalytic converter becomes clogged, you’ll likely notice several signs indicating that your vehicle’s performance is compromised. These symptoms may range from subtle changes in engine behavior to more severe issues that require immediate attention. Here are the key symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter:
1. Loss of Power and Poor Acceleration
One of the most noticeable signs of a clogged catalytic converter is a significant loss of power. The restriction in exhaust flow caused by the blockage leads to increased backpressure in the engine. As a result, the engine struggles to expel exhaust gases, which reduces its ability to take in fresh air for combustion. This can cause sluggish acceleration, poor throttle response, and a general lack of power.
2. Rattling Noise
If the catalytic converter is severely damaged or clogged, you may hear a rattling noise coming from underneath your vehicle. This noise is often caused by pieces of the converter’s honeycomb structure breaking apart and moving around inside the housing.
3. Dark or Excessive Exhaust Smoke
A clogged catalytic converter may cause the engine to run rich, leading to incomplete combustion. As a result, you may notice dark or excessive smoke coming from the exhaust, indicating that the converter is unable to properly filter emissions.
4. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
When the catalytic converter is clogged, the engine has to work harder to maintain the same level of performance, which leads to increased fuel consumption. If you notice that your vehicle’s gas mileage has decreased significantly, it could be due to a clogged catalytic converter restricting the flow of exhaust gases.
5. Check Engine Light
A clogged catalytic converter can trigger the check engine light. Modern vehicles are equipped with oxygen sensors that monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If the sensors detect that the converter is not functioning properly, they will send a signal to the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU), causing the check engine light to come on.
Diagnosing a Clogged Catalytic Converter
If you suspect that your catalytic converter is clogged, it’s important to have it diagnosed by a qualified mechanic. Here are some common methods used to diagnose a clogged converter:
1. OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your vehicle’s engine control unit. Codes related to the catalytic converter (such as P0420 or P0430) indicate that the converter is not functioning properly and may be clogged.
2. Backpressure Test
A backpressure test measures the exhaust flow before and after the catalytic converter. High backpressure readings indicate that the converter is clogged and restricting exhaust flow.
3. Temperature Test
A temperature test involves measuring the temperature at both the inlet and outlet of the catalytic converter. If the outlet temperature is significantly lower than the inlet temperature, it indicates that the converter is not allowing exhaust gases to flow freely, which may be due to a blockage.
How to Fix a Clogged Catalytic Converter
Once a clogged catalytic converter has been diagnosed, the next step is to determine the best course of action. Here are some common solutions for addressing a clogged converter:
1. Catalytic Converter Cleaner
In some cases, using a catalytic converter cleaner may help dissolve carbon deposits and improve the converter’s efficiency. Catalytic converter cleaners are added to the fuel tank and work by burning off carbon buildup as the engine runs. This solution is most effective when the converter is only partially clogged and is still functioning.
2. Replace the Catalytic Converter
If the catalytic converter is severely clogged or damaged, the only solution may be to replace it. Catalytic converters contain precious metals, which can make replacement expensive, but it’s necessary to restore engine performance and ensure that your vehicle complies with emissions standards.
3. Address Underlying Issues
If the clogged catalytic converter is the result of engine problems like misfires, oil leaks, or excessive fuel consumption, it’s important to address these issues to prevent the new converter from becoming clogged as well.
How to Prevent a Catalytic Converter from Becoming Clogged
Preventing a catalytic converter from becoming clogged is much easier (and less expensive) than dealing with a clogged converter after the fact. Here are some tips to keep your catalytic converter in good condition:
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Regular engine maintenance, such as oil changes, spark plug replacement, and fuel injector cleaning, can help prevent issues that lead to a clogged catalytic converter.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: If you notice that your engine is misfiring, consuming too much fuel, or leaking oil, have it inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel can help reduce carbon buildup in the engine and catalytic converter, keeping the exhaust system clean.
Conclusion
A clogged catalytic converter can cause a range of problems, from poor engine performance to increased emissions. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, it’s important to have your vehicle checked by a mechanic to prevent further damage. Regular maintenance and addressing engine issues promptly can help prevent your catalytic converter from becoming clogged and ensure that your vehicle runs efficiently.
