Catalytic converters play a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases from your car’s exhaust system into less harmful substances. However, like any part of your vehicle, the catalytic converter can develop issues over time, one of the most common being clogging. But can a catalytic converter get clogged? The answer is yes, and if left unresolved, it can lead to poor engine performance and even engine damage.
In this article, we’ll explore how a catalytic converter can get clogged, what signs to look out for, and how to fix or prevent this issue from occurring.
What Causes a Catalytic Converter to Get Clogged?
Catalytic converters can become clogged for a variety of reasons, most commonly due to a buildup of carbon deposits or contaminants entering the exhaust system. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Carbon Buildup
Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate inside the catalytic converter, particularly if your engine is running rich (burning too much fuel). These deposits block the honeycomb structure within the converter, reducing its efficiency and leading to clogging.
2. Engine Misfires
Engine misfires can result in unburned fuel entering the exhaust system. When this happens, the excess fuel can ignite inside the catalytic converter, causing it to overheat and become damaged. The damage can lead to a clogged converter that restricts the flow of exhaust gases.
3. Oil or Coolant Leaks
Oil or coolant leaking into the exhaust system can contaminate the catalytic converter, causing it to become clogged. When oil or coolant enters the combustion chamber and burns in the exhaust system, it creates a thick residue that can block the catalytic converter’s internal structure.
4. Excessive Fuel Consumption
A malfunctioning oxygen sensor or fuel injector can cause your engine to consume more fuel than necessary. Excess fuel leads to incomplete combustion, which results in carbon and soot buildup within the catalytic converter, causing it to clog over time.
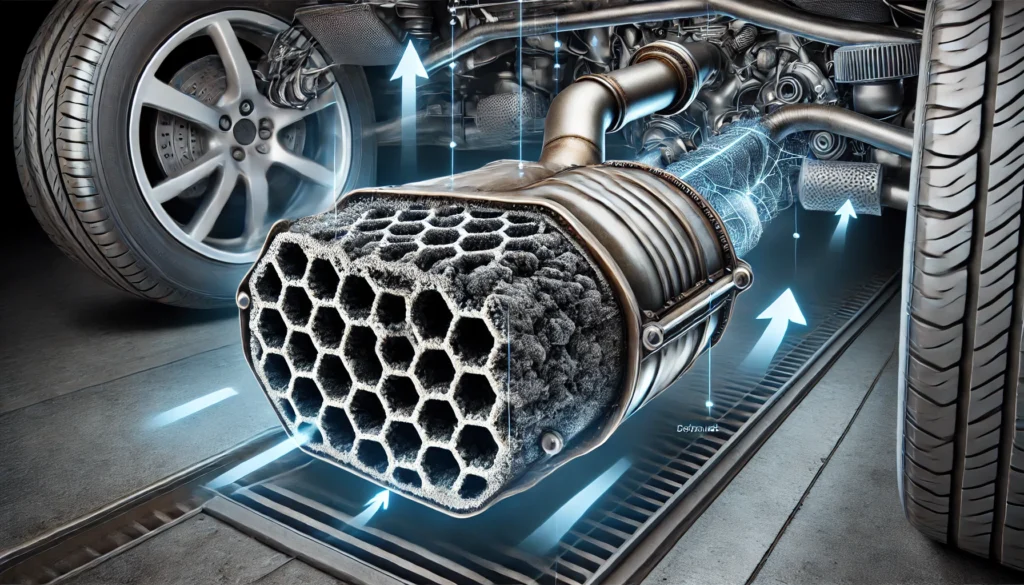
Symptoms of a Clogged Catalytic Converter
A clogged catalytic converter can cause a range of issues with your vehicle. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you address the problem before it causes more serious damage. Here are the most common symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter:
1. Loss of Power and Sluggish Acceleration
If your vehicle feels sluggish or unresponsive when accelerating, it could be a sign that your catalytic converter is clogged. Blockages in the converter create backpressure, which reduces the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases and take in fresh air for combustion. This leads to a noticeable drop in performance, especially when trying to accelerate quickly.
2. Rattling Noises
A severely damaged or clogged catalytic converter may produce a rattling sound coming from underneath the vehicle. This noise occurs when the internal components of the converter break apart due to overheating or physical damage.
3. Dark Exhaust Smoke
A clogged catalytic converter can cause unburned fuel to pass through the exhaust system, leading to dark or excessive smoke coming from the tailpipe. This is a clear sign that the converter is not filtering emissions properly and could be blocked.
4. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
If you notice that your vehicle is burning more fuel than usual, it could be a sign of a clogged catalytic converter. A blockage causes the engine to work harder, which results in increased fuel consumption. If your gas mileage has dropped noticeably, a clogged converter may be the culprit.
5. Check Engine Light
A clogged catalytic converter often triggers the check engine light. Modern vehicles are equipped with sensors that monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If the sensors detect that the converter is not functioning as it should, they will alert the engine control unit (ECU), causing the check engine light to illuminate.
Diagnosing a Clogged Catalytic Converter
If you suspect that your catalytic converter is clogged, it’s important to have it diagnosed by a professional mechanic. Here are some common methods used to diagnose a clogged catalytic converter:
1. OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can detect diagnostic trouble codes related to the catalytic converter. Codes such as P0420 or P0430 indicate that the catalytic converter’s efficiency has dropped below the manufacturer’s threshold, potentially due to clogging.
2. Backpressure Test
A mechanic can perform a backpressure test to measure the exhaust flow before and after the catalytic converter. If there is a significant increase in backpressure, it indicates that the converter is clogged and needs attention.
3. Temperature Test
A temperature test involves measuring the temperature at the inlet and outlet of the catalytic converter. A significant difference between the two readings suggests that the converter is restricting exhaust flow, which could be due to clogging.
How to Fix a Clogged Catalytic Converter
If your catalytic converter is clogged, there are a few potential solutions, depending on the severity of the clogging:
1. Catalytic Converter Cleaner
In some cases, a catalytic converter cleaner can be used to remove carbon deposits and improve exhaust flow. These cleaners are added to the fuel tank and help burn off carbon buildup in the catalytic converter as the engine runs. This method works best for converters that are partially clogged but still functional.
2. Replace the Catalytic Converter
If the catalytic converter is severely clogged or damaged, the only solution may be to replace it. Replacing a catalytic converter can be costly due to the precious metals used in its construction, but it’s essential for restoring your vehicle’s performance and meeting emissions standards.
3. Address Underlying Engine Issues
If your catalytic converter became clogged due to engine problems, such as misfires, oil leaks, or fuel issues, it’s important to address these underlying issues to prevent the new converter from becoming clogged as well.
Preventing Catalytic Converter Clogs
Preventing a clogged catalytic converter is easier than dealing with the problem after it occurs. Here are some maintenance tips to help keep your converter in good condition:
- Regular Maintenance: Regular engine tune-ups, oil changes, and fuel system cleanings can help prevent carbon buildup in the catalytic converter.
- Address Engine Problems Promptly: If you notice issues like engine misfires, oil leaks, or increased fuel consumption, get them fixed as soon as possible to avoid damaging the catalytic converter.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel with detergent additives can help reduce carbon deposits and keep your catalytic converter functioning properly.
Conclusion
A clogged catalytic converter can cause serious issues with your vehicle, from poor engine performance to increased emissions. While it’s possible to fix a partially clogged converter with a cleaner, severe clogs usually require replacement. Recognizing the symptoms early and addressing the problem promptly can save you from more expensive repairs down the road. Regular vehicle maintenance and addressing engine issues as they arise can help prevent catalytic converter clogging and keep your vehicle running efficiently.
