A clogged catalytic converter can cause significant issues with your vehicle’s performance, including reduced power and efficiency. But how to check a catalytic converter is clogged? In this article, we’ll walk you through the signs of a clogged converter and the steps you can take to diagnose the issue effectively.
Signs of a Clogged Catalytic Converter
Recognizing the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter is the first step in diagnosing the problem:
- Reduced Engine Performance
- A clogged catalytic converter restricts exhaust flow, leading to a noticeable drop in engine power and acceleration. If your car feels sluggish or unresponsive, the converter could be the culprit.
- Dark or Black Smoke from the Exhaust
- Excessive backpressure caused by a clogged converter can result in incomplete combustion, leading to dark or black smoke coming from the exhaust.
- Check Engine Light
- The check engine light may turn on if the vehicle’s sensors detect an issue with the exhaust system, including a clogged catalytic converter.
- Rattling Noise
- A rattling sound coming from underneath your vehicle could indicate that the internal components of the catalytic converter have broken apart due to excessive pressure.
- Overheating
- A clogged converter can cause the engine to overheat due to restricted airflow. You may notice unusually high engine temperatures or even experience engine stalling.
How to Check if a Catalytic Converter Is Clogged
If you suspect your catalytic converter is clogged, here’s how you can check:
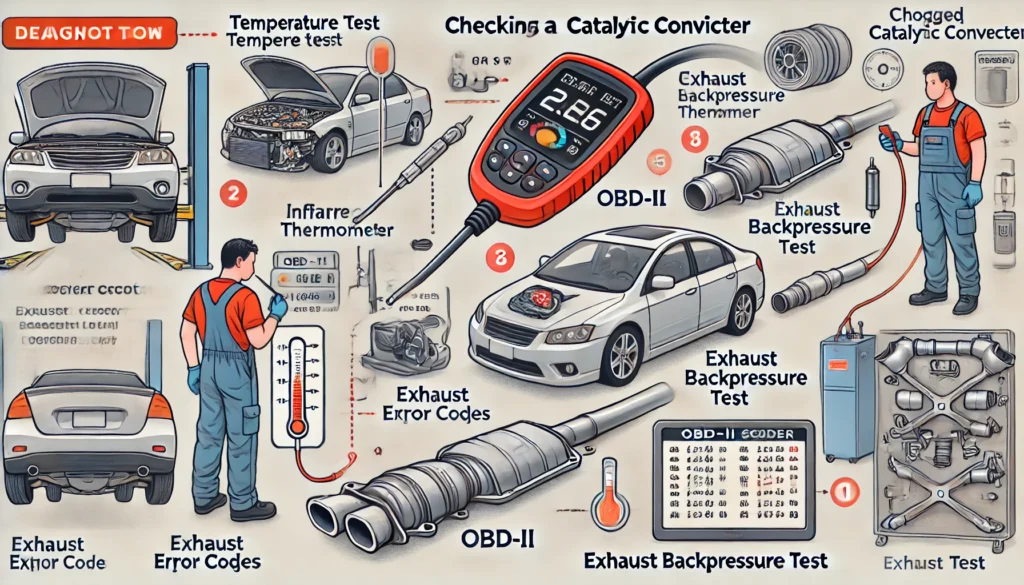
1. Perform a Temperature Test
- Using an infrared thermometer, measure the temperature at both the inlet and outlet of the catalytic converter. A healthy converter should have a higher temperature at the outlet than at the inlet. If the temperatures are the same or the outlet is cooler, the converter is likely clogged.
2. Use an OBD-II Scanner
- An OBD-II scanner can help diagnose issues related to the catalytic converter. Look for error codes like P0420 or P0430, which indicate that the converter is not functioning efficiently.
3. Exhaust Backpressure Test
- A backpressure test measures the exhaust pressure before and after the catalytic converter. High pressure readings before the converter suggest that it is clogged and restricting the exhaust flow.
4. Check for Physical Damage
- Inspect the catalytic converter for any visible signs of damage, such as dents, cracks, or excessive rust. Physical damage can cause or contribute to clogging.
5. Listen for Rattling Sounds
- Start your vehicle and listen for any unusual rattling sounds coming from underneath. This noise could be caused by broken pieces inside the catalytic converter due to clogging.
When to Replace a Clogged Catalytic Converter
If the diagnostic tests confirm that your catalytic converter is clogged, replacing it is often the best course of action. Driving with a clogged converter can lead to more severe engine problems and increased emissions, so it’s important to address the issue promptly.
Conclusion
Checking if a catalytic converter is clogged involves recognizing the symptoms, performing temperature and backpressure tests, and using diagnostic tools like an OBD-II scanner. By following these steps, you can accurately diagnose a clogged converter and take the necessary steps to maintain your vehicle’s performance.
