If you’re experiencing issues with your vehicle’s performance or fuel efficiency, you might be wondering, “How do you check a catalytic converter?” The catalytic converter is a vital component of your car’s exhaust system, responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. When this part begins to fail, it can lead to a variety of problems, from sluggish acceleration to an increase in emissions. In this blog post, we will explore how you can check your catalytic converter to determine if it’s functioning properly or if it needs attention.
What is a Catalytic Converter?
The catalytic converter is located in your vehicle’s exhaust system, usually between the engine and the muffler. It contains a honeycomb structure coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These materials facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful emissions such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. Ensuring that your catalytic converter is functioning correctly is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s efficiency and complying with emissions regulations.
How to Check a Catalytic Converter
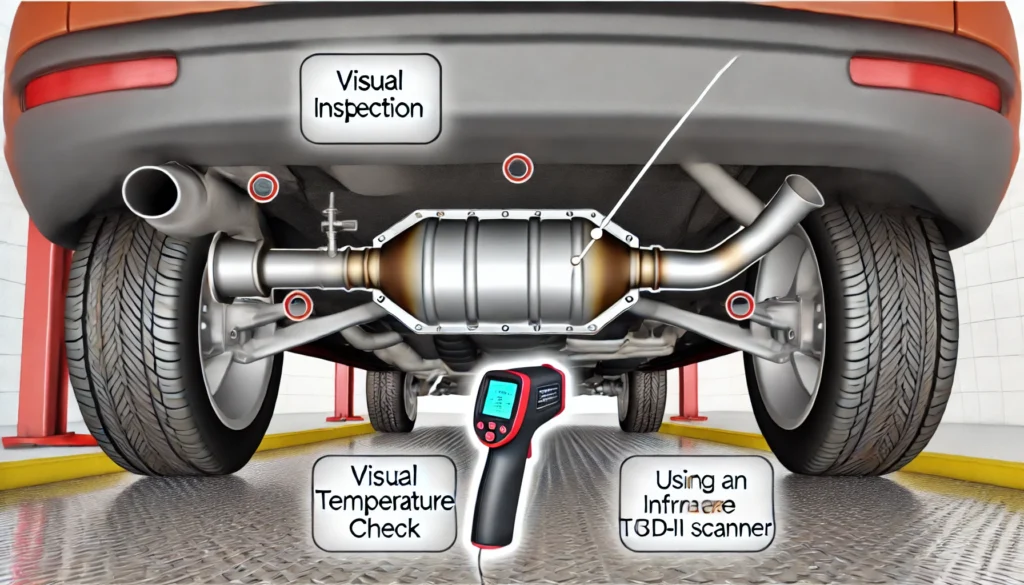
- Visual Inspection
The first step in checking your catalytic converter is to perform a visual inspection. Begin by locating the converter under your vehicle. Look for any obvious signs of damage, such as dents, rust, or discoloration. These could indicate physical damage or overheating, which can compromise the converter’s performance.
- Listen for Unusual Sounds
A bad catalytic converter can sometimes produce unusual sounds, especially when the car is idling or accelerating. If you hear a rattling noise coming from underneath your vehicle, it could mean that the internal components of the converter have broken apart. This rattling sound is often a sign that the converter needs to be replaced.
- Check the Temperature
You can also check the catalytic converter’s temperature to determine if it’s functioning properly. Start your vehicle and let it run until it reaches operating temperature. Using an infrared thermometer, measure the temperature at the front and rear of the converter. If the converter is working correctly, the rear should be hotter than the front. If the temperatures are the same or if the front is hotter, it could indicate a blockage or inefficiency.
- Backpressure Test
A backpressure test can help determine if the catalytic converter is clogged. This test requires a pressure gauge and a fitting to attach it to the oxygen sensor port. After removing the oxygen sensor, attach the gauge and start the engine. If the pressure is higher than normal, it indicates a blockage in the catalytic converter.
- Use of an OBD-II Scanner
Modern vehicles are equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) system that monitors the performance of various components, including the catalytic converter. By connecting an OBD-II scanner to your vehicle, you can check for trouble codes related to the catalytic converter. Codes like P0420 or P0430 indicate that the converter is not operating efficiently.
- Emissions Test
One of the most straightforward ways to check the catalytic converter’s performance is through an emissions test. During this test, the levels of pollutants in the exhaust are measured. If the catalytic converter is failing, it won’t effectively reduce emissions, leading to higher pollutant levels and a failed test.
What to Do If Your Catalytic Converter Is Bad
If any of these checks indicate that your catalytic converter is bad, it’s important to address the issue promptly:
- Replacement: In most cases, a bad catalytic converter will need to be replaced. While this can be expensive, it’s necessary for ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently and complies with emissions regulations.
- Preventive Maintenance: To prevent future issues, regular vehicle maintenance is key. This includes timely oil changes, using high-quality fuel, and addressing engine issues like misfires or oil leaks promptly.
Conclusion
Checking your catalytic converter is an important part of maintaining your vehicle’s health and ensuring it meets emissions standards. By following the steps outlined above, you can identify potential issues early and take the necessary actions to keep your vehicle running smoothly. If you suspect your catalytic converter is failing, it’s crucial to consult with a professional mechanic to avoid further damage and ensure your car remains roadworthy.
