If your vehicle has been acting up lately, you might be wondering, “How to diagnose a bad catalytic converter?” The catalytic converter is a crucial component of your car’s exhaust system, designed to reduce harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. When this part starts to fail, it can lead to a variety of issues that affect your car’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. In this blog post, we’ll explore the steps you can take to diagnose a bad catalytic converter, the tools you may need, and the symptoms to watch out for.
Understanding the Role of the Catalytic Converter
Before diving into the diagnosis process, it’s important to understand what the catalytic converter does. Located between the engine and the muffler, the catalytic converter contains a honeycomb-like structure coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These materials help convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful emissions such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can lead to increased emissions and poor vehicle performance.
Common Symptoms of a Bad Catalytic Converter
Before diagnosing, it’s essential to recognize the symptoms that might indicate a bad catalytic converter:
- Reduced Engine Performance: A clogged or damaged catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, leading to sluggish acceleration and reduced power.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: If your vehicle is using more fuel than usual, it might be because the catalytic converter is not processing exhaust gases efficiently.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light might illuminate if the vehicle’s sensors detect abnormal levels of exhaust gases.
- Dark or Black Exhaust Smoke: This can indicate incomplete combustion, often due to a malfunctioning catalytic converter.
- Rattling Noise: A broken or damaged catalytic converter can produce a rattling noise, especially when the vehicle is idling or accelerating.
- Sulfur or Rotten Egg Smell: This odor indicates that the catalytic converter is not processing exhaust gases properly.
Steps to Diagnose a Bad Catalytic Converter
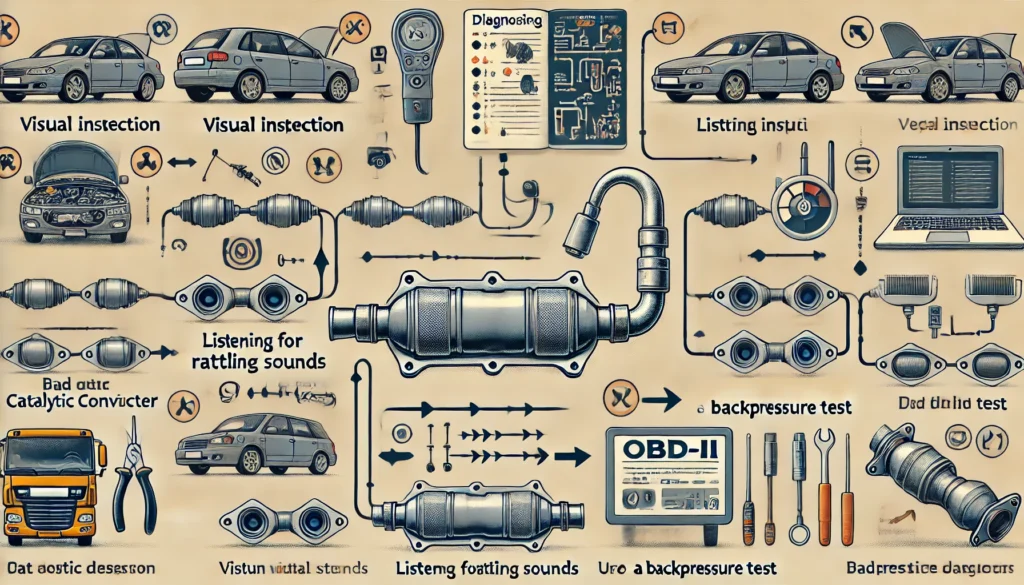
Diagnosing a bad catalytic converter can be done through a combination of visual inspection, listening for specific sounds, and using diagnostic tools. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Visual Inspection
- Check for External Damage: Look under your vehicle to inspect the catalytic converter. If you notice any dents, rust, or physical damage, it could be a sign that the converter is malfunctioning.
- Examine the Exhaust Smoke: While the engine is running, observe the color of the exhaust smoke. Dark or black smoke might indicate that the catalytic converter is not processing exhaust gases efficiently.
2. Listen for Rattling Sounds
- Start the engine and listen closely near the catalytic converter. If you hear a rattling noise, it could mean that the internal components of the converter have broken apart, which is a clear sign of a bad catalytic converter.
3. Use an OBD-II Scanner
- Check Engine Light Codes: If your check engine light is on, use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble codes. Codes related to the catalytic converter include P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold) and P0430. These codes suggest that the catalytic converter is not functioning properly.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: The OBD-II scanner can also provide readings from the oxygen sensors located before and after the catalytic converter. If the readings from these sensors are similar, it indicates that the converter is not effectively reducing emissions.
4. Backpressure Test
- A backpressure test can help determine if the catalytic converter is clogged. Using a pressure gauge, measure the exhaust backpressure before and after the catalytic converter. Higher-than-normal backpressure readings indicate a clog in the converter.
5. Temperature Test
- Using an infrared thermometer, check the temperature of the exhaust pipe before and after the catalytic converter. A healthy converter should have a higher temperature at the outlet than at the inlet because it is converting exhaust gases. If the temperature is the same or lower, it indicates that the converter is not working properly.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some diagnostic steps can be performed at home, others may require the expertise of a professional mechanic. If you’re unable to diagnose the problem or if the catalytic converter needs to be replaced, it’s best to consult with a professional to ensure your vehicle is running efficiently and safely.
Conclusion
Diagnosing a bad catalytic converter is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and ensuring it meets emissions standards. By recognizing the symptoms and using the right diagnostic tools, you can determine if your catalytic converter is malfunctioning and take the necessary steps to address the issue. Regular vehicle maintenance and prompt attention to engine problems can help extend the life of your catalytic converter and prevent costly repairs.
